Appearance
Architectural Deep Dive: The Lifecycle of an AI Job
The Simple Platform's $ai API provides a deceptively simple developer experience. Behind that single function call lies a powerful, distributed, and highly secure architecture designed for enterprise-grade scale and reliability. This document provides a look "under the hood" at the end-to-end lifecycle of a single $ai.extract call involving a document, corresponding to the numbered steps in the diagram below.
Understanding this flow reveals why Simple can offer guarantees of security, performance, and determinism that legacy platforms cannot match.
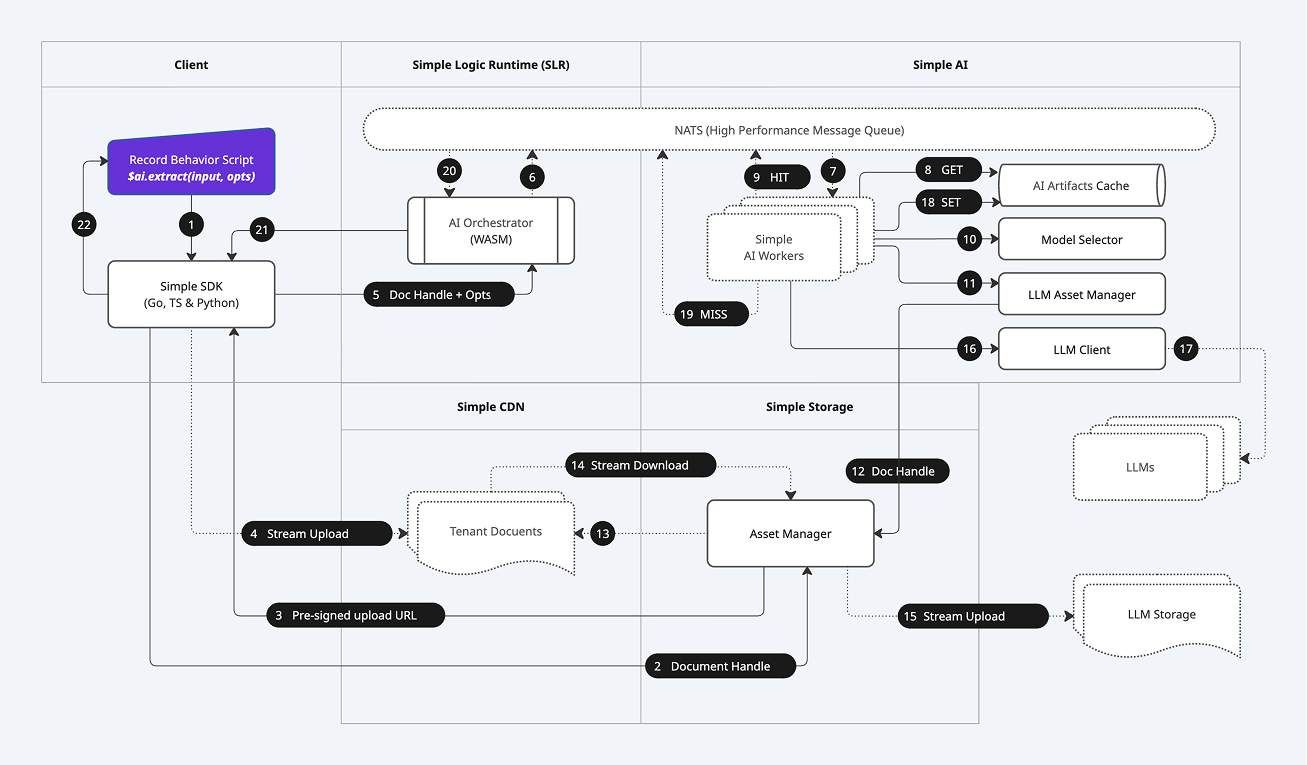
High-Level Phases
The entire process can be understood in four major phases:
- The Secure Request: The client securely uploads a file and initiates the AI task without the file content ever passing through the application server.
- Durable Job Orchestration: The request is transformed into a durable, asynchronous job, published to a high-performance message queue, and picked up by a scalable pool of AI workers.
- Secure Asset Federation & Execution: The AI worker orchestrates a secure, stream-through transfer of the file to the external AI provider and manages the execution, validation, and caching of the AI task.
- The Guaranteed Response: The final, validated result is returned to the original calling script, ensuring a consistent and reliable outcome.
Step-by-Step Breakdown
Phase 1: The Secure Request (Client-Side)
This phase occurs entirely on the client, leveraging our Zero-Trust architecture.
- 1. API Call: A developer's Record Behavior Script calls the
$ai.extract()function via the Simple SDK. - 2. Document Handle Creation: If the document is new, the SDK first communicates with the platform to obtain a
Document Handle, a secure pointer to the file's metadata. - 3. Pre-signed Upload URL: The Simple Platform returns a secure, short-lived, pre-signed URL that grants the client temporary, direct write-access to a specific location in Simple's secure, tenant-isolated storage.
- 4. Direct Stream Upload: The client's browser uploads the file's content directly to the provided URL. The file content never passes through our application servers, dramatically enhancing security and scalability.
Phase 2: Durable Job Orchestration (Server-Side)
Once the file is securely stored, the server-side orchestration begins.
- 5. Secure RPC to the Logic Runtime: The SDK sends the final
Document Handleand the AI options (prompt, schema, etc.) via a secure RPC call to the AI Orchestrator, which runs inside the Simple Logic Runtime (SLR). - 6. Publish Job: The AI Orchestrator constructs a durable job definition and publishes it to a high-performance message queue (NATS). It then awaits a response on a unique reply topic.
- 7. Job Consumption: One of the many available Simple AI Workers in a distributed pool consumes the job from the queue. This architecture allows the system to scale horizontally to handle tens of thousands of concurrent AI tasks.
Phase 3: Secure Asset Federation & Execution (Simple AI Service)
The AI Worker now takes over, managing the core AI task and interaction with the external provider.
- 8. Check AI Memcache: The worker first checks the AI Artifacts Cache (our AI Memcache) to see if this exact operation has been performed before.
- 9. Cache Hit: If a valid, cached result exists, it is immediately published back to the NATS reply topic (Step 20), providing a near-instant, zero-cost response. The flow ends here for this request.
- 10. Model Selection: On a cache miss, the worker's Model Selector intelligently chooses the optimal AI model based on the user's request (e.g.,
lite,large), cost, and current provider availability. - 11. Asset Management: The LLM Asset Manager is tasked with making the internal document available to the external AI provider.
- 12. Fetch Document Handle: It retrieves the
Document Handlefor the file to be processed. - 13. & 14. Secure Stream Download: The Asset Manager initiates a secure, streaming download of the file directly from Simple Storage.
- 15. Secure Stream Upload: In parallel, it initiates a stream-upload of that file to the external LLM's Storage. Crucially, the file content is piped directly from our storage to the provider's storage without ever being fully loaded into the memory of the AI service. This zero-memory-footprint approach allows for the processing of massive files and is a key security and performance feature.
- 16. & 17. Execute LLM Call: With the asset now available to the provider, the LLM Client makes the final API call, providing the prompt, schema, and the pointer to the uploaded asset.
- 18. Set AI Memcache: The raw result from the LLM is received, validated, and stored in the AI Artifacts Cache for future requests.
Phase 4: The Guaranteed Response
The final result is now ready to be returned to the user.
- 19. Job Result (Miss): The AI Worker publishes the final, structured result to the NATS reply topic for the original request.
- 20. Orchestrator Receives Result: The AI Orchestrator, which was awaiting this message, receives the result.
- 21. Return to SDK: The result is sent back to the Simple SDK that made the initial call.
- 22. Update UI: The SDK returns the structured JSON data to the Record Behavior Script, which can then safely populate the form fields, triggering a UI update for the user.
The Simple Advantage: An Unmatched Architecture
This end-to-end, fully managed process provides benefits that are architecturally impossible on legacy platforms:
- Unparalleled Security: With Zero-Trust direct-to-storage uploads and zero-memory-footprint asset federation, your sensitive data has a minimal attack surface.
- Infinite Scalability: The decoupled, message-queue-based worker architecture is designed for massive, enterprise-grade parallelism from the ground up.
- Extreme Efficiency: The AI Memcache dramatically reduces cost and latency, while the streaming data pipelines handle large files with minimal resource consumption.
- Guaranteed Reliability: By treating AI tasks as durable jobs with automated retries and a self-healing worker pool, the system ensures that your business logic completes, even if a provider has a transient failure.
Next Steps
Now that you've seen the architecture, learn about the practical implementation details.
- The Document Lifecycle: Understand how Simple's Zero-Trust architecture handles file uploads from a developer's perspective.
- API Reference: Get detailed documentation for the
$ai.extract()and$ai.summarize()methods. - Return to Introduction: Go back to the main AI & Document Intelligence overview.